[ad_1]
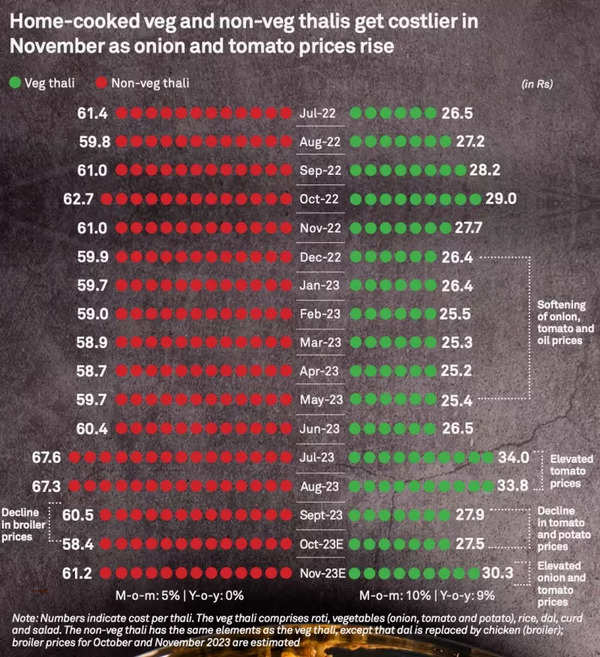
The surge is linked to a notable 58% and 35% on-month hike in onion and tomato prices, driven by festive demand and reduced kharif season output due to unpredictable rainfall, the rating agency said.
Notably, the non-vegetarian thali costs rose slower than vegetarian thali costs on-month. This can be attributed to a slight 1-3% decrease in broiler prices, constituting roughly 50% of the non-vegetarian thali cost.Year-on-year, the vegetarian thali expenses increased by 9%, fueled by a substantial 93% and 15% surge in onion and tomato prices. Pulses’ prices, forming about 9% of the veg thali cost, also spiked by 21%.
Home cooked thali cost trends by CRISIL
The vegetarian thali includes roti, vegetables (onion, tomato, and potato), rice, dal, curd, and salad. The non-vegetarian thali features similar components to the vegetarian version, replacing dal with chicken (broiler).
These thali cost estimations by CRISIL are based on input prices across various regions in India. The monthly variations reflect the impact on the average consumer’s spending, shedding light on the key ingredients influencing the thali cost—cereals, pulses, broilers, vegetables, spices, edible oil, and cooking gas.
In July, retail inflation surged to a 15-month peak of 7.44%, notably driven by food price inflation reaching 11.5%. This is the highest level for food price inflation in over three and a half years. Additionally, despite government actions like export restrictions and pulse imports aimed at curbing food inflation, the figure remained elevated at 6.61% in October.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its monetary policy review is expected to keep the key policy rates unchanged, given the sticky nature of retail inflation, the impact of erratic monsoon, and better than expected GDP data alleviating concerns of higher interest rates impacting growth.
[ad_2]
Source link

